RETINOL CELL
1 Reviews
Vitamin A food supplement - Retinol. Specially formulated by our experts to :
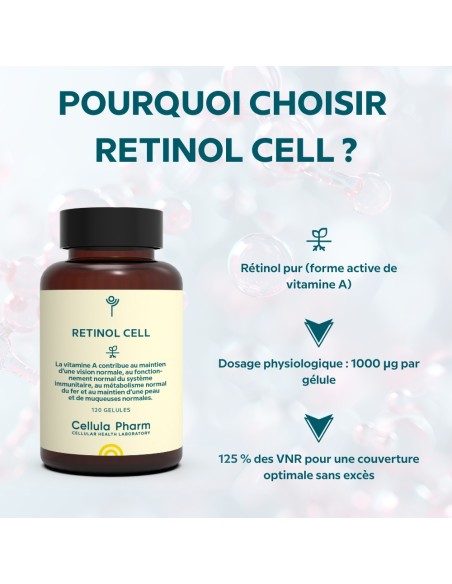
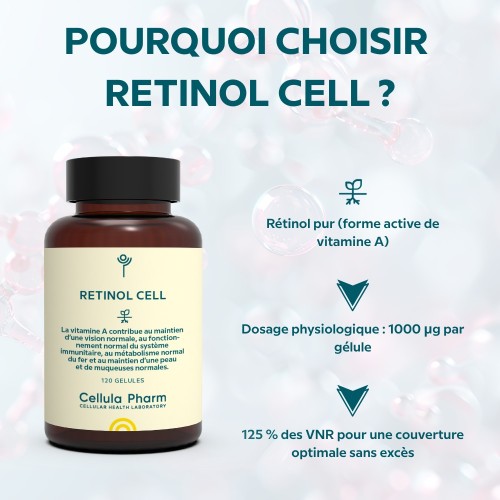
- Ensure proper assimilation thanks to the active form of vitamin A: retinol
- Provide optimal dosage: 1000 µg (125% of daily requirements)
- 4-month program
- Additive-free
- Vegan
Composition per daily dose:
| Actives: | 1 capsule | VNR* |
| Vitamin A | 6. 6 mg | |
| - of which Retinol | 1000 µg | 125 % |
| Excipients: Organic acacia fiber, vegetable capsule (HPMC) | ||
Ingredients for 1 dose (1 capsule):
Organic acacia fiber, vegetable capsule (HPMC), retinyl acetate (Retinol), rapeseed oil.
For optimum effectiveness, take 1 capsule a day. Take every day.
Dietary supplement.
- Does not replace a varied and balanced diet or healthy lifestyle.
- Do not exceed recommended doses.
- Keep out of the reach of young children. Adult only.
- Do not give to children under 10.
- Do not consume in case of intolerance or allergy to any of the components.
- Store in its packaging, away from light, heat and moisture.
1 Reviews
Excellent pour stimuler la régénération de la peau, agit comme un exfoliant ! top
You might also like